

Therefore, each student’s right hand will appear on the left for his/her partner. Explain that they are looking at an anterior (front) view of their partner student’s body. To demonstrate this to your class, ask each student to face another student and raise his or her right hand. Ask, Does one part feel thicker or more muscular than another? īecause most diagrams show the anterior (front) view, the right side of the heart appears on the left side of the diagram. Have students locate, and then gently press on, the upper and lower chambers of their heart specimens. Ask, How does the heart feel when you touch it? If using sheep hearts, explain to students that the heart’s texture has been altered by the preservation chemicals. Have students examine the heart specimens. Have each Materials Manager pick up a tray of materials for his or her group. Monitor students, as some people may begin to feel a little uncomfortable during the procedure.ĭistribute copies of the “Heart Dissection” page and have students read it within their groups. Inform students that there will be no blood involved in the dissection (it is clotted). Safety Note: Be sure all students wear gloves and safety goggles, even if they only will touch the heart. Tell students that they will be examining chicken or sheep hearts similar to the ones they viewed in the videos previously. Record their questions to refer to at the end of this activity. Ask students to share any questions they still have about the heart’s structure or function. Procedure and Extensions Part One: Exterior of the Heartĭiscuss students’ previous explorations of the exterior and interior of the heart. Or visit the Virtual Heart Web site () to provide a three-dimensional class demonstration of the heart’s structures. Note: This activity may be conducted as a class demonstration. Make copies of all student sheets listed under "Materials per Student." Have students perform the dissections in groups of four. Make pins with masking tape flags for each group, or have students make their own. Place all necessary dissecting materials on paper plates or trays, with one set of materials for each student group. Keep the sheep hearts in tightly sealed plastic bags.

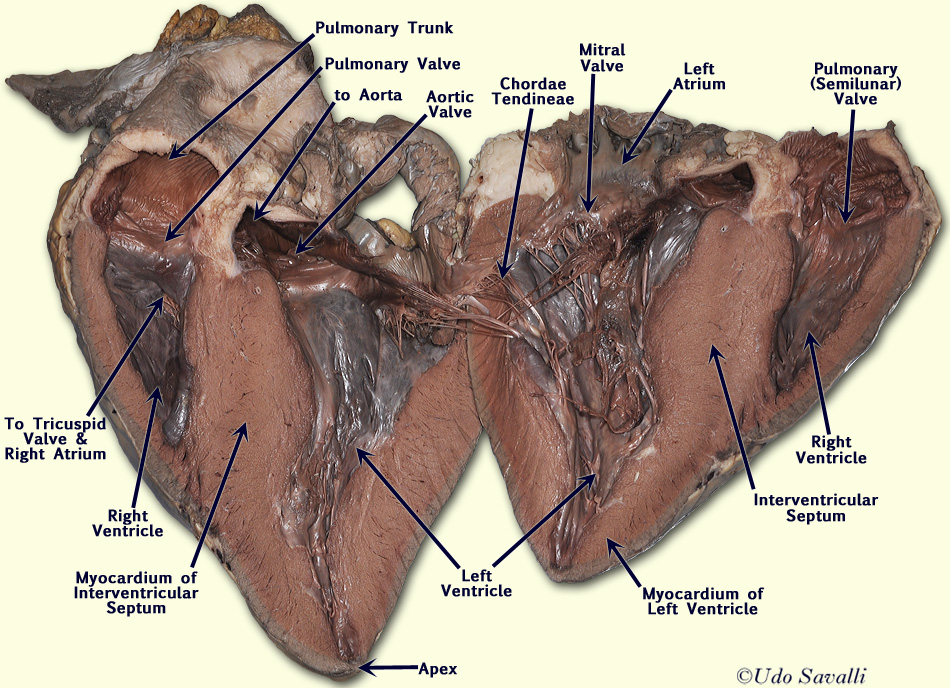
Sheep hearts are preserved and can be used for several weeks. Purchase chicken hearts from a grocery store or order sheep hearts from a biological supply company. Pair of dissecting scissors, plastic knife or scalpelĬopy of "The Heart: External," and "Inside the Heart," (see "Lesson Media" tab, above). Sheep heart (preserved) or chicken heart (fresh) PowerPoint ® slides or transparencies of all student sheets Materials and Setup Teacher Materials (see Setup, below) Students also should note that there are several one-way valves in the heart that prevent blood from moving backward from the atria into the veins, from the ventricles back into the atria, and from the arteries back into the ventricles. The walls of the atria are not as thick as those of the ventricles. As students examine and dissect a heart, be sure they note the thick, muscular, elastic walls that allow the ventricles to pump blood effectively throughout the body. The two upper chambers, the atria, receive blood returning from the body (right atrium) and the lungs (left atrium), and pass it into the lower chambers, the ventricles, so that they can pump it to all other areas of the body. The heart is a double pump with four chambers. Additional signals about pace can come from the brain (nervous system) and hormones (endocrine system). Together, the SA and AV nodes regulate contractions of the ventricles and atria, and allow the heart to work as an efficient double pump. The signal from the sinoatrial node spreads to another small bundle of nervous tissue, the atrioventricular node (AV node), located in the heart wall between the two chambers on the right side of the heart.

A small bundle of nervous tissue, called the sinoatrial node (SA node), in the wall of the right atrium initiates each contraction and serves as a “pacemaker,” setting the rate and timing of heartbeats. Due to this important characteristic, the heart does not require a signal from the brain or spinal cord every time it needs to contract.
Cardiac muscle cells are able to contract on their own, without receiving stimulation from the nervous system. The heart is made mostly of a special kind of muscle, known as cardiac muscle, which is very resistant to fatigue.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
